BLOG
World Water Supply Shortage of 40% by 2030?! Water risks on the rise
- Eco Friendly
2023.03.14
In early January, the Eurasia Group, SU geopolitical risk consulting firm, released its report, Top Risks 2023, which identified the world’s most pressing ten global risks, one of which was ‘Water Stress’. The world's water resources are limited, and the United Nations predicts a 40% global water supply shortfall by 2030 if current consumption and production patterns remain unchanged.
In addition, according to the World Bank's 2021 report, Water Risk and Its Impact (Ebb and Flow), the Middle East and North Africa, the world’s most water-stressed regions, 60% of the population currently live in water-stressed areas and are expected to suffer record economic losses of an estimated 6 ~ 14% by 2050.
In this article, we will introduce the growing global water risk and its impact on corporate activities.
Limited water resources
Many parts of the world are facing a water crisis, which include depletion of water resources and deterioration of water quality. India, for example, faces an unprecedented water crisis with shortages of domestic, agricultural, and industrial water. Even in Brazil, where fresh water is abundant, the Parana River basin, where hydroelectric dams and reservoirs are located, is experiencing its worst drought in more than 100 years. The drought has affected production of key Brazilian crops such as coffee, corn, sugarcane, and oranges. In 2021 coffee bean production fell by 20 ~ 30%, pushing up global market prices by as much as 60%. About 60% of China's groundwater is considered contaminated and unsuitable for domestic use, posing a threat to the country's economic growth. In addition, according to NASA analysis, 13 of the world’s 37 largest aquifers are depleted, putting water availability in certain areas at risk.
These threats affect all sectors of society, and companies risk having their production activities disrupted by an unstable water supply. The problem is particularly acute in regions with high water stress (where water supply and demand are tight).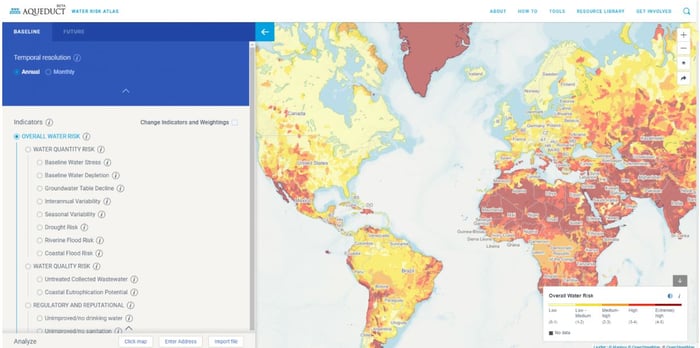
Source: Aqueduct Global Maps (World Resources Institute)
A 2030 water stress scenario projected if global greenhouse gas emissions continue to increase at its current rate. The World Resources Institute defines water stress as "the ratio of total water intake withdrawals to the sum of available renewable surface water and groundwater supplies." The higher the water stress level, the greater the competition among water users.
Business activities are related to water resources in two ways: impact and dependence. In other words, while water intake and drainage associated with business activities affect the quantity and quality of water resources, at the same time they depend on a sufficient quantity and quality of water resources to sustain their business operations. The risks associated with water resources vary depending on the industry, type of business, size and location of the business, etc., but examples of possible risks in terms of the two relationships of impact and dependence are shown in the table below (source: CDP).
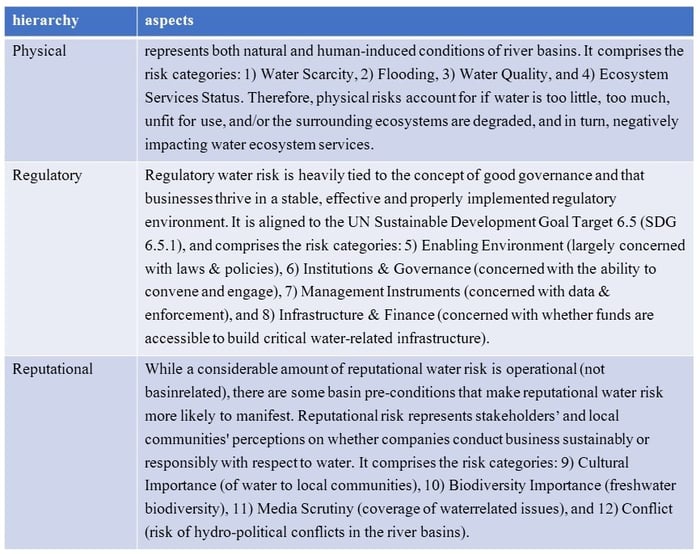
Source: WWF
"WATER RISK FILTER METHODOROGY DOCUMENTATION, JANUARY 2023
Many companies and investors, both in developed and emerging countries, are facing growing water risks, highlighting the reality that water is no longer a free and limitless resource. It is predicted that future population growth and economic development, as well as the intensified climate change, will cause water resource shortages and water stress in an increasing number of regions.
Disclosure of Initiatives on Water Resources Issues
Water risks, which can directly or indirectly not only have a financial impact on corporate activities but also damage the brand image, is increasingly recognized as a management issue that companies cannot afford to ignore. Recently, institutional investors have become increasingly interested in the financial impact of water risk on companies. In order to sustain their business, companies are required to understand their own water risks and that of their suppliers and disclose this information to investors.
As the ESG Rating of MSCI and FTSE, one of the world's leading stock indexes, is based on the content of integrated reports and annual financial reports, the disclosure of information on water risk and initiatives related to water risk is important in this context.
A growing number of companies are responding to CDP Water Security, a global information disclosure program on corporate water risks by CDP, run by an international non-profit organization based in the UK. To help investors understand a company’s sustainability, it evaluates the company's water risk initiatives from multiple perspectives through answers to a variety of questions, and companies are evaluated assigned to one of four categories, A, B, C, or D according to their level of initiatives.
According to the CDP Water Security Report 2021, released in January 2022, 37 Japanese companies were selected for the A-list, the highest rating. There were 102 companies selected for the A-list worldwide, meaning Japan had the largest number of A-list companies in the world (a total of 361 Japanese companies were sent the project-based questionnaire, to which 223 companies (62%) responded) .
In the CDP 2022 Score released in December 2022, more than 330 companies worldwide were recognized as grade A either in CDP Climate Change, Forestry, or Water Security. 91 of the A-list companies were Japanese companies, again the largest number in the world.
Tackling Water Risks
As water resources are essential for the production activities of many companies and for the production of the raw materials they procure, the widening gap between supply and demand of water resources has a direct impact on corporate profits. The impact of "water" on corporate finances has recently received increasing attention from institutional investors.
In addition to water, environmental and social issues can also bring opportunities, not just risks, to business activities. As an example, water risk responses can reduce costs by working to reduce water consumption. Companies are expected to meet the needs of institutional investors by preparing for the increasing water risks in the future and enhancing information disclosure through such initiatives as water risk assessment covering the entire value chain, setting targets that take into account the characteristics of the regions relevant to their business activities, and contributing to solving water-related social issues through products and services.
Maritime industry companies are not included in the CDP Water Security Questionnaire (only the railroad industry is nominated in the transport sector), and has not yet attracted much attention in terms of water risk, but water risk response is a global trend that needs to be closely monitored.
|
Water business in MOL Business proposals and considerations of fresh water transportation and the supply of fresh water by desalination vessels were made to address the global issue of water shortages under MOL Incubation Bridge (New business ideas proposal programme). ■ Comments from person in charge
Photo: Floating Desalination Vessel (FDV) with our partner “EnviroNor” |
MOL is committed to addressing environmental issues through co-creation with stakeholders. You can find materials summarizing our environmental initiatives in line with Environmental Vision 2.1, which sets more concrete quantitative targets for a long-term GHG emission reduction roadmap. We invite you to read about the wide range of our initiatives.
Recommended Articles
2022.07.05
- General Shipping
2021.04.13
- Energy
2025.03.18
- General Shipping
2021.08.07
- Eco Friendly
Latest Articles
2026.02.02
- Eco Friendly
- General Shipping
2026.01.20
- Eco Friendly
- General Shipping
2025.12.09
- Eco Friendly
- General Shipping

.png?width=700&height=394&name=Initiative%20on%20Environment%20CTA%20(1).png)








