BLOG
Cryo-Powered Regas System for FSRU (1)
- Energy
2021.10.18
FSRU, one of the solution services provided by Mitsui O.S.K. Lines(MOL), involves research and development to improve fuel efficiency and reduce CO2 emissions. This is called "Cryo-Powered Regas" system for FSRU. In March 2020, MOL and Daewoo Shipbuilding & Marine Engineering Co., Ltd. (DSME) received Approval in Principle (AIP) from Bureau Veritas Marine (Singapore) ; and successfully demonstrated a verification test at DSME Tamaura shipyard in August 2021.
This blog introduces the mechanism of Cryo-Powered Regas system for FSRU and the efforts that we have made so far.
# MOL Channel "Cryo-Powered Regas" System for FSRU by MOL and DSME"
Promotion Movie can be seen by clicking on the image above.
LNG, heated by seawater to become an energy source for regasification itself
Today, natural gas is mainly used as a raw material for thermal power generation, and it has become an important energy source in the world. However, in many countries, their own production is low and they rely on imports mainly from Asia, Europe and North America.
When natural gas is liquefied, it is reduced to a volume 1/600 of the original volume, so it is liquefied to at extremely low temperature of approximately -160 °C in order to transport as LNG (liquefied natural gas). Natural gas is often transported through long pipelines overseas (the world's longest pipeline between Russia and Ukraine is 4,600 km long). On the other hand, in Asia, including Japan, LNG is mostly transported by ships. A vessel is constructed like a tanker with a huge thermos bottle on its belly, which is filled with LNG. LNG, arrived at LNG receiving terminal by ship is heated by seawater at a coastal area and re-gasified for use as an energy source. A single tanker can carry about 70,000 ~ 120,000 tons of LNG, which can generate electricity for about 50 million households for a day.

Proposal for More efficient power generation by Installation of Regasification Facility at Sea
Demand for LNG is growing around the world and is expanding in developing countries. However, the construction of an onshore LNG facility in a coastal area requires considerable amount of time and cost, which is a significant burden for developing countries. Then, we believe that the FSRU (Floating Storage and Regasification Unit) could be one of the solution.
As its name suggests, FSRU is a floating regasification facility at sea. There is no need for a large land area to build a base in the coastal area because the facility is constructed like a ship itself. Therefore, this has the merit of being able to introduce regasification facilities at low cost and in a short period of time. In addition, it has been difficult to construct an onshore base in shallow waters because a certain depth of water is required for LNG carriers to call at the base. However, FSRU can be installed offshore and deliver LNG to and from LNG carriers.
Currently, about 40 FSRUs are in operation worldwide.

Further proposals for reducing the environmental impact in FSRU
As mentioned above, seawater is used to return liquid LNG to its original gas form (regasification). Because LNG is at a very low temperature of about -160 °C, there is a temperature difference of about 180 °C between seawater and LNG, and it can therefore, be regasified without heating. This does not mean that regasification does not require any external energy at all, though. In order to operate pumps and other equipment to move the gas, small amount of electric power is required a minimum. This power has traditionally been secured by using the generators on board, however, to reduce this power consumption, we devised a method of generating electricity by using “cold energy”, which was previously released into the ocean or the atmosphere and discarded.
"Cold energy" is the energy that generated by using the difference in temperature when something in a cryogenic state returns to normal temperature. Though there are several methods of generating electricity by using cold energy, MOL has been working on the method that transferred “cold energy” to another heat medium (organic medium) which has low boiling point to create a temperature difference from the steam in the heat medium vaporized by the heat of the seawater, thereby rotate a turbine efficiently and generate power. This method is called the " Organic Rankine Cycle." It is a technology that enables efficient power generation with a medium to low temperature heat source, and its mechanism is similar to that of a steam turbine, but differs greatly in terms of its use of organic media with a low boiling points to evaporate.
By introducing this method in FSRU, it can be expected to generate approximately 4~5MW of power in the regasification process when it performs in a standard size of FSRU. This electric power is equivalent to the power of one large wind turbine, and by using this electric power, the fuel required for the regasification process and CO2 emissions can be reduced by up to 55%. In addition, it also results in huge cost reduction for fuel.
Cryogenic power generation is being actively introduced in the regions with high sea temperatures(such as Southeast Asia and South America), because it improves power generation more efficiently.
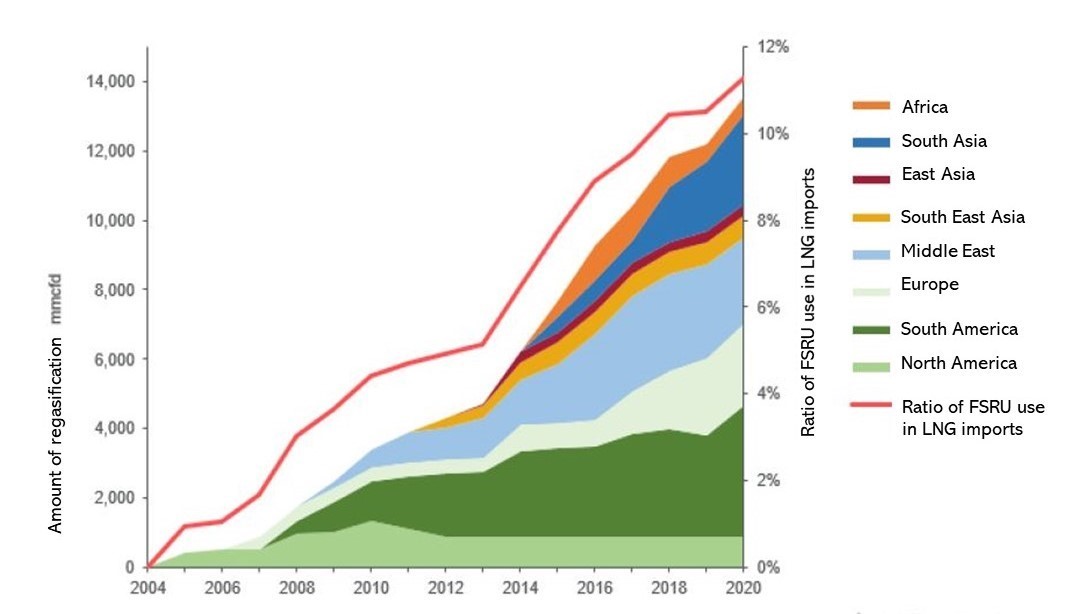
Data from Wood Mackenzie and Created by MOL
Trial and Error for Implementation of "Cryo-Powered Regas System for FSRU"
For more than 40 years, this kind of power generation by "cold energy" has been used to generate electricity at a coastal onshore LNG terminal. However, the biggest difficulty in developing such a system at sea, are the tremors caused by waves, which made it difficult to ensure stable rotation of turbines for power generation. In addition, miniaturization of the system is also a prerequisite for installation on ships. We asked a number of manufacturers to develop a turbine generator, but did not receive any favorable responses. However, we found out that Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Marine Machinery & Equipment Co, Ltd., which manufactures steam turbine generators for ships, had the know-how and asked for their cooperation in finding a solution to this problem. We made a test module that was scaled down from the actual machine, and verified with actual refrigerant whether the small turbine could generate the appropriate amount of electricity by exchanging heat. After repeated trial and error like these verifications, "Cryo-Powered Regas System for FSRU " was finally realized. In terms of miniaturization, it performs ideally for use on ships.

Image of Turbine Generator
(by Mitsui Heavy Industries Marine Machinery & Equipment Co, Ltd.)
In 2018, IMO adopted GHG initial strategy for ships and currently the entire maritime transportation industry is accelerating its efforts to reduce fuel consumption and CO2 emissions. The use of cold energy for LNG is a major step forward in addressing these environmental issues.
Toward the Realization of the Decarbonized Society
Japan started importing natural gas in 1969. At that time, natural gas still accounted for only about 1% of domestic energy supply, but it has been increasing ever since, and by the beginning of 2000, the volume had increased to the same level as coal. Furthermore, when the ratio of nuclear power generation in the energy supply shrank due to the Great East Japan Earthquake, natural gas attracted attention as a fuel for thermal power generation, and demand for natural gas increased significantly. As a result, effective use of natural gas has begun to spread worldwide.
Why is natural gas attracting so much attention now? This is because natural gas emits the least amount of carbon dioxide when it burned, compared to other fossil fuels such as coal and oil, and also because it does not generate sulfur oxides (SOx), which can lead to air pollution and cause asthma and acid rain. Another merit is that there is almost no generation of "soot and dust," which are fine particles contained in smoke generated when materials are burned.
As the world moves toward the decarbonized society, there is great expectation for natural gas as an energy resource that can replace coal and oil. However, there remains a number of challenges ahead to secure future energy resources. Mitsui O.S.K. Lines will continue to take an active role in overcoming new challenges and help realize the sustainable society in the future.
As part of these initiatives, we are promoting the conversion of fuels used in ships from conventional heavy oil to next-generation fuel with lower GHG emissions. The features of these new fuels are summarized in " Next Generation Clean Fuels" which can be downloaded here.


Writer:Ayu
Joined MOL in 2008. I’ve been in charge of operating oil tankers and bulk carriers for abt 7 years. And now I am currently involved in the operation of this site, in the marketing department.
I'm also in charge of managing MOL’s LinkedIn account. Please follow us! My favorite is K-Pop music :)
Recommended Articles
2022.07.05
- General Shipping
2021.04.13
- Energy
2025.03.18
- General Shipping
2021.08.07
- Eco Friendly
Latest Articles
2026.01.20
- Eco Friendly
- General Shipping
2025.12.09
- Eco Friendly
- General Shipping
2025.12.03
- General Shipping











